Vitamins B12: How Much is Too Much?
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin with numerous benefits for normal bodily function.
Some people neglect the notion that taking high doses of supplements than the prescribed amount can have negative health consequences. Others have wondered how much of this vitamin is too much due to this behavior.
This article will go over the recommended daily doses of vitamin B-12, the implications of taking excess vitamin B12, and how vitamin B-12 may affect pregnancy.
What Is Vitamin B12 Used For?

Vitamin B12 is a part of the essential B vitamin that promotes good health. It is a water-soluble vitamin that helps to regulate the neurological system, the human brain, and blood production. B12 is a typical product of bacterial fermentation. It impacts DNA synthesis and is in charge of body cell metabolism.
Vitamin B-12 is needed for the proper function of your brain, blood cells, neurons, and other organs. B12 can help treat vitamin B-12 deficiency and pernicious anemia– a condition in which your intestinal tract has difficulty absorbing vitamin B-12.
Vitamin B-12 can help cure hyperhomocysteinemia, which puts your veins and arteries in danger when taken, and folic acid and vitamin B6. Taking vitamin B-12, folic acid, and vitamin B6 together may help you avoid developing age-related macular degeneration, an eye illness.
Vitamin B12 In Its Many Forms And Dosages
Oral Supplements:
Liquid and tablet forms of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) are available in various shapes and quantities. A typical daily oral dose is around 1,000 mcg.
Nasal Spray:
Start with a single spray of 500 mcg in one nostril once a week. Following a review of your lab results, your doctor may alter your dose.
Injection:
A standard dose is 100 micrograms. It may be necessary to take it every day less frequently as your health improves. This dosage depends solely on your medical condition. After reviewing medical information and lab results, your doctor will alter your dose. Individuals with pernicious anemia may need B12 injections of about 100 mcg per month.
Pros of Vitamin B12
The following are some essential advantages of consuming B12:
B12 Prevents Shrinking Of The Brain
This is one intrinsic factor of Vitamin B12 in older adults. Taking B12 might help preserve their brains from shrinking and boost their White blood cells (particularly the T-cells).
It Prevents Eye Diseases
Vitamin B 12 and B6 supplementation can help prevent age-related macular degeneration, a type of eye illness.
B12 Are Also Food Additives
The cyanocobalamin supplement in vitamin B 12 is used as a food additive because of its low cost of manufacture and stability.
It Also Boosts Energy Conversion
Vitamin B12 is a B-vitamin that aids in naturally converting energy from food. The supplement helps to maintain a healthy life.
Vitamin B 12 Plays A Key Role In The Creation Of DNA
The water-soluble element cyanocobalamin aids in protecting our blood cells, aid nerve function, and creates DNA. It helps to mend the stomach lining.
It Reduces Depression And Improves Moods
The vitamin helps regulate your mood by manufacturing and metabolizing serotonin molecules, which helps prevent depression.
Treatment For Cyanide Poisoning And Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 hydroxocobalamin is a vitamin B12 supplement that can prevent and treat vitamin B12 deficiency. Because it combines with cyanide to generate cyanocobalamin, it’s also utilized to treat illnesses linked to toxic levels of cyanide.
It Boosts Blood Circulation
B12 is necessary for red blood cell formation, boosting the body’s oxygen supply.
It Can Reduce Birth Abnormalities In The Neural Tube
Vitamin B 12 aids in the creation of body cells, minimizing the effects on the neural tube. To prevent the birth of children with birth abnormalities, the administration of folic acid to pregnant mothers is essential.
Cons Of Vitamin B12
There are hazards associated with any drug. Even if the medication is beneficial, you may experience unwanted side effects. The following are some of the drawbacks of taking Vitamin B12:
Interaction Between vitamin B 12 And Other Drugs
Although vitamin B 12 is harmless, it can interact with other medications, reducing the vitamin’s absorption. Certain drugs like Glucophage, which is used to treat diabetes, chemotherapy, and stomach acid, cause vitamin deficiency.
Overdose Can Result In
Overdose Vitamin B12 injections can induce diarrhea, stomach bloating, and nausea, among other things.
Adverse Health Effects
Injections of vitamin B12 can produce adverse effects in some people, such as chest aches, rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing, muscle weakness or pain, or skin rashes. If you notice any of the abovementioned symptoms, you should seek medical attention.
Vitamin B 12 Can Contribute To Blindness
Vitamin B 12 can result in optic nerve damage and cause blindness if you have a genetic eye illness or are allergic to cobalt.
It Can Result In Constriction Of The Blood Vessels
Combining vitamin B12, folate, and vitamin B6 can promote blood channel narrowing after a coronary stent or surgery.
It Increases Red blood cells (RBCs)
It can cause a rise in the number of dysfunctional red blood cells, which can have catastrophic consequences for people.
Tolerable Upper Intake Level Of Vitamin B12
As a result of its low toxicity, B12 has no Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL). The Upper Intake Level is the highest daily intake of a vitamin that is unlikely to cause serious side effects in the general population (UL).
Your body excretes everything it doesn’t use through pee; therefore, the establishment of the B12 threshold isn’t stable. Increased B12 supplementation, on the other hand, links to several unfavorable side effects.
Megadoses of the vitamin have been linked to breakouts of acne and rosacea, a skin ailment marked by facial redness and pus-filled pimples. However, it is necessary to know that the bulk of these trials used high-dose injections rather than oral supplementation.
Harmful Consequences of Overdose Intake
There is also some indication that very high doses of B12 can have harmful health consequences in people with diabetes or kidney disease.
Diabetic nephropathy– a medical term that means the loss of kidney function owing to diabetes, can result in a faster reduction in renal function for individuals with the condition when given high doses of supplements of B12, according to a 2010 study.
Furthermore, those who received excessive amounts of B vitamins had an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and mortality compared to those who received a placebo. More recent research, however, is needed to back up this notion.
Another research on pregnant women found that high doses of vitamin supplements increased the chance of autism in their unborn child.
Despite evidence that B12 supplementation can have serious health consequences, studies have demonstrated that daily oral doses of up to 2,000 mcg are safe and effective in treating B12 deficiency.
The RDA for vitamin B12 is 2.4 mg for both men and women, with pregnant and breastfeeding women needing more.
The recommended daily intake (RDI) of vitamin B12 for men and women is 2.4 mg, while pregnant and breastfeeding women require more.
What Should You Look For While Buying Vitamin Supplements?
Vitamin B 12 supplements are pretty safe, even at doses many times the recommended upper limit. This recommendation is because it is a water-soluble vitamin and is readily excreted in the urine. B12, like all vitamins, functions best when combined with a group of other essential nutrients.
Unless you’ve been diagnosed with a deficiency, it’s advisable to take it in a multivitamin. In that instance, a doctor may prescribe large doses to cure the deficiency before switching to a reduced maintenance dose.”
If you need to take a vitamin B12 supplement, you can do the following:
Make Sure It Is Simple To Consume
If you know you have difficulties swallowing pills, a sublingual medication that dissolves beneath your tongue or a spray or liquid may be beneficial.
Take Special Note of the Dosages
For most people, the daily recommended dietary requirement of vitamin B 12 is 2.4 micrograms, with 2.6 and 2.8 micrograms if you’re pregnant or breastfeeding. However, your doctor may recommend a different dosage based on your specific ailment unless you’ve discussed it with your doctor.
Check If There Are Any Other B deficits.
People who require additional vitamin B12 are often deficient in other B vitamins, like the vitamins B9 and B6. Carry out blood tests and consult a healthcare professional to see if a B complex is okay to consume.
Opt-Out For Methylcobalamin
The majority of vitamin B 12 pills include cyanocobalamin, which contains trace levels of cyanide. It’s also ineffective compared to methylcobalamin supplementation. When cyanocobalamin-based B12 supplements are in the body, the liver must first eliminate the cyanide molecule before attaching a methyl group to produce methylcobalamin, the physiologically active, tissue-ready version. This process is challenging for a damaged liver to carry out.
However, according to research, the methylcobalamin form is more efficiently utilized, especially for individuals with liver disease or loss of kidney function.
Pay Close Attention To Labels
The type of B12 should be specified. Switch to safer “methyl” or new “hydroxyl” versions instead of “cyano” even though it’s often the most affordable. Also, seek either the capsule or liquid form that gets absorbed under the tongue because they operate faster than other forms.
The Best Vitamin B12 Supplements
While you can acquire vitamin B 12 through foods, one of the best Vitamin B12 supplements can help you get your prescribed dose.
Here are the best vitamin B12 supplements to help you get your B12 fix:
Pure Encapsulations Methylcobalamin 1,000 mcg
Product Description
Due to the supplement being utterly devoid of questionable filler substances and capacity to raise energy levels substantially, people who take 1 to 3 of these capsules daily highly suggest them. They’re also gluten-free.
Pros
- Non-GMO certification
- Absence of additives
- Dairy-free, soy-free product
- Suitable for both vegetarian and vegan consumption
Cons
- Individuals allergic to cobalt can’t use this product.
Nature Made
- Supplement Form: cyanocobalamin
- Type: soft gel
- Dosage: 1,000 mcg
- Certification: cGMP certified, USP verified
Product Description
These soft gels are simple to take and have little to no aftertaste, making them an easy addition to your daily routine—even if you’re not usually a supplement user. In a month or two, if you combine it with a glass of water and a meal, you may notice a reduction in weariness.
Pros
- Gluten-free
- Free of additives
- Very Effective
Cons
- Not suitable for everyone
- It contains gelatin and soy
- It is costly
Live Conscious Methylcobalamin Vegan B12 Drops
- Supplement Form: Methylcobalamin
- Type: Liquid
- Dosage: 5,000 mcg
- Certification: GMP certified
Product Description
These easy-absorption vegan supplement sources are mainly from plant food sources and aid in digestion and better hair, skin, and nails while improving cognition and the nervous system.
These vegan drops are an excellent alternative for those who dislike taking pills. Put a citrus-flavored drop under your tongue and drink a glass of water, and you’ll be on your way to increased energy and a sharper memory.
Pros
- Third-party certification
- Non-GMO Product
- Preservative and additives free
- Fit for vegans and lactose intolerant individuals.
Cons
- The dose might be too high for some individuals.
Natrol Vitamin B12 Fast Dissolve Tablets
- Supplement Form: cyanocobalamin
- Type: fast dissolve tablet
- Dosage: 5,000 mcg
- Certification: cGMP certified
Product Description
These fast-dissolving pills don’t require any water, and you may consume them anywhere, at any time. It is a fantastic alternative for food allergies because it is lactose-free, soy-free, gluten-free, and devoid of egg, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, and peanuts. To top it up, they’re incredibly cost-effective.
Pros
- It is possible to dissolve it in the tongue without using water.
Cons
- Added sugar alcohol
- May cause digestive discomfort
Jarrow Formulas Methyl B-12
- Supplement Form: Methylcobalamin
- Type: Chewable lozenges
- Dosage: 5,000 mcg
- Certification: Third-party certification, cGMP certified
Product Description
This supplement is for forgetful people; you need to take it every few days, and the body absorbs this supplement quickly because it’s chewable and has a high amount of B12.
Pros
- It provides a nice energy boost
- Aids in fatigue relief
Cons
- It contains sugar and alcohol.
Symptoms Of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Because vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms are so widespread, knowing if your levels are too low can be challenging.
Vitamin B 12 Deficiency can cause problems with balance, disorientation, depression, and poor memory. There are also potential risks of deficiency leading to dementia over time and lifelong nervous system damage. That means it’s critical to address a deficiency as soon as possible.
The following are more prevalent symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, which is a condition in which your body cannot make red blood cells as needed by your body as a result of a lack of B12:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Tingling or numbing feeling of the limbs
- Difficulties walking
- Low or lack of appetite
- Weakness of the muscles
- Increased heart rate
- Insistent weight loss
- Constant tiredness or fatigue.
- Fretfulness
What Is The Optimal Dosage of B12?
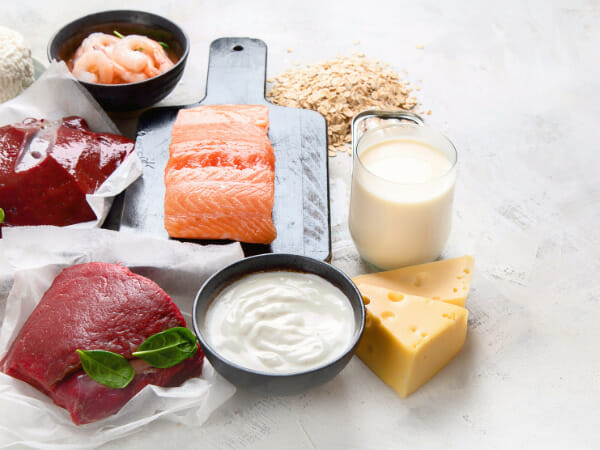
Healthy people who aren’t in danger of B12 deficiency should get all of the B12 they need from a nutrient-dense, balanced diet.
This vitamin can be found in various animal products, including eggs, red meat, chicken, seafood, milk, yogurt, fortified cereals, nutritional yeast, and non-dairy products.
Individuals taking drugs that alter B12 absorption, pregnant or breastfeeding women, vegetarians, and individuals with medical conditions that will reduce B12 absorption or increase the need for B12 should consult their doctor about supplementation.
Furthermore, evidence from population research suggests that B12 deficiency is frequent in older adults, which is why adults over 50 should consider taking supplements.
Advisable Vitamin B12 Dosage
While consuming large quantities of up to 2,000 mcg is safe in treating B12 insufficiency, it’s always recommended to avoid taking too much of any vitamin, primarily when its intake is not related to essential health concerns.
A very high dose of B12 is unlikely to harm most people. However, it would help to avoid high-dose consumption unless prescribed by a medical professional.
Reach out to a healthcare professional if you suspect you are deficient in B12. They will be able to recommend a treatment plan based on your level of deficiency.
While no UL exists for B12, your body’s ability to absorb the vitamin depends on how much it needs.
For example, only ten mcg of a 500-mcg B12 dose is absorbed in persons who don’t have a deficit.
Conclusion
You can consume B12 even without having a deficiency.
Although there is no indication that excess vitamin B-12 supplementation has any adverse side effects, it is best not to overdose on the vitamin.
Most healthcare professionals do not recommend taking more than the quantity indicated in prenatal or daily multivitamins unless a person has a condition that causes vitamin B-12 insufficiency. Although vitamin B12 doses of up to 2,000 mcg of vitamin B 12 are generally considered safe, it is best to visit a doctor to determine whether supplementation is necessary.
However, individuals allergic to cobalt or have Leber’s illness should avoid taking Vitamin B-12. Most people may meet their B12 requirements by eating a nutrient-dense diet. However, some people, such as older adults, strict vegetarians, other individuals with diet restrictions, and individuals with low vitamin B-12 levels causing them concern, should discuss supplements with their doctor.
As an Amazon Associate INQUIRER.net will earn from qualifying purchases.