How 3D Printing Is Revolutionizing How We Make Things
Imagine that you just got a new iPhone, so you wanted a new case. You searched the internet for options, but none of them fit your style. Fortunately, 3D Printing allows you to create the perfect iPhone case and nearly anything else!
Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D Printing lets people create a model of small objects. As a result, it is much easier to create test samples of a particular product or make one yourself. Learn this skill to adapt to the new era of manufacturing.
Start by checking the wide range of applications for 3D Printing, also known as additive manufacturing. After that, we will explore the different ways of 3D Printing. We will discuss the tips you need to start printing 3D models at home.
Applications of 3D Printing
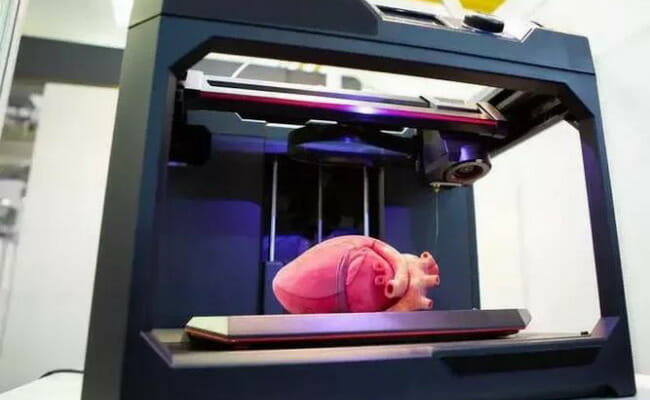
Photo Credit: technologymagazine.com
Making products from a printer may seem futuristic, but this method has been around since the 80s. Back then, people called it Rapid Prototyping (RP) technologies.
The Cambridge Dictionary defines a prototype as “the first example of something, such as a machine or other industrial product. Based on this definition, RP tech involves quickly creating a sample of an object.
Traditional manufacturing methods work by creating each part individually and then assembling them into a final product. That is why modern factories have assembly lines designated for specific components.
They’re great for creating a product en masse because they just follow a template. If you need to make something from scratch, these production lines are not helpful.
Companies constantly find new ways to expand via new goods and services. Of course, they will have to test the products before being offered to customers.
Additive manufacturing or 3D Printing facilitates research and development by fabricating prototypes within hours. Without it, a sample product would take days to create.
The technology was so expensive that only significant firms could afford to use it. Nowadays, you can find a lot of 3D printers for home use.
What’s more, 3D Printing is an instrumental tool for the automotive, aerospace, medical, and jewelry industries. Let us look at how rapid prototyping tech helps the following sectors:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Medical
- Consumer goods
- Industrial goods
- Education
1. Aerospace
Airplanes have improved considerably since the bold flight of the Wright brothers. Nowadays, modern aircraft consists of several complex parts, making it difficult to design new ones.
These components require specialized tooling equipment that can be costly. Fortunately, 3D Printing allows engineers to fabricate the parts faster and cheaper.
The technology also lets them reduce the weight of these components. Weight is a significant feature since airplanes need to be as light as possible to achieve flight.
What’s more, modern 3D printing methods prevent waste. The engineers just have to place the material needed for their parts.
This rapid manufacturing method can create objects that assemble into more complex products. As a result, it reduces the duration required to produce components.
Also, 3D Printing can help repair aircraft much quicker. Rapid prototyping transitioned into rapid manufacturing as the technology progressed. Nowadays, you can create finished products with 3D printers, not just samples.
For example, selective laser sintering can print metal objects. 3D-printed metal parts can become durable enough for real-life applications.
The aerospace industry can now make spare parts more conveniently with rapid manufacturing processes. Some firms like the French manufacturer Latécoère use 3D Printing to create custom tooling equipment.
The company took six weeks to create tools via traditional methods. With 3D Printing, Latécoère can fabricate production equipment within two days, reducing the lead time by 95%.
2. Automotive
Car manufacturers spend billions of dollars making sure their vehicles are safe. That’s why they make sure to design automobiles that will not harm or endanger passengers.
Similar to aircraft, the cars of today have many complicated parts. Making a new car from scratch for testing purposes is expensive, so manufacturers turn to 3D Printing.
Modern rapid manufacturing processes can turn any digital design into a tangible object. If any part doesn’t meet expectations, engineers can quickly print a better one.
In other words, the technology facilitates research and development in the automotive industry. What’s more, 3D Printing improves customization while reducing costs.
A luxury car brand can use the technology to create personalized vehicles for clients. The company can simply print their preferences, such as a custom steering wheel.
The aerospace and automotive industries share similar purposes for 3D Printing. A car manufacturer can use the technology to fabricate spare parts quickly.
Rapid manufacturing methods also make it easier to conduct repairs. Automotive companies could simply print a new part instead of having one custom-made for a specific client.
3. Medical
Modern medicine uses technology to improve its tools and services. It provides quality care by making them more suitable for each patient’s needs.
Nowadays, 3D Printing enables the medical sector to achieve higher precision, affordability, and speed. It can now create implants and prosthetics with less time and money.
Specifically, the dental industry now uses 3D printing technology for dental impressions. As a result, its laboratories can make products like crowns and bite splints that accurately match a patient’s body.
Highly accurate and customizable surgical guides are now possible with 3D Printing. For example, Lima Corporate uses the technology to make hip replacements that can seamlessly become a permanent part of a patient’s body.
What’s more, 3D printing methods like material jetting help create accurate organ replicas. They allow surgeons to practice on a model of a patient’s body before operating.
As a result, the procedures become faster and safer. Moreover, 3D Printing enhances medical research by enabling the creation of bioprinted tissue.
These are thin layers of tissue that medical experts use to test therapies and medicines. This method eliminates the need to conduct harmful clinical tests.
This production method also speeds up the construction of emergency response structures. For example, California-based Mighty Buildings uses 3D Printing to build portable hospitals with 95% fewer labor hours than conventional means.
4. Consumer goods
The best products undergo rigorous testing before they appear on store shelves. As mentioned earlier, making prototypes with traditional manufacturing methods can be a hassle.
Fortunately, 3D Printing makes research and development more convenient nowadays. Engineers and designers can test multiple versions of a product without taking a long time to create each one.
As a result, companies can offer new products and services much faster than before. Some businesses even applied the method to pilot product testing.
This method lets consumers try a product before releasing it to the market. To illustrate how 3D Printing facilitates this process, let’s look at Ruffles chips as an example.
PepsiCo wanted to try new shapes for the potato chips to make them more tasty and crunchy. With 3D Printing, they could make individual crisps with different forms until test respondents identify the best one.
The process also lets PepsiCo push out new Ruffles flavors faster. Besides boosting R&D, 3D Printing reduces production cost and duration.
For example, California-based Franco Bicycles prints the body frame of its Emery ONE electric bike. With traditional manufacturing, the process takes 18 months, but 3D Printing slashes that down to a couple of days.
This process also allows for products that are not possible with conventional means. For example, the jewelry industry uses 3D Printing to make intricate details too nuanced or complex for traditional methods.
This production method also helps clothing brands to create tailor-made apparel quickly. A 3D printer could also make personal protective equipment based on your preferences and measurements.
5. Industrial goods
Traditional manufacturing processes require specific tools and equipment. With the help of 3D Printing, making these products is faster and cheaper than ever.
The 2018 State of Industry report from Sculpteo says that 52% of industrial firms prefer 3D Printing to cut down on lead times. In other words, the process helps them make new parts faster than before.
Like the jewelry industry, 3D Printing allows for industrial products that were not possible with old methods. Also, the process lets companies quickly make backup parts.
For example, the Siemens Mobility RRX Rail Service Centre prints on-demand components. As a result, it minimizes the cost of replenishing and maintaining inventory.
Industrial production also relies on electronic components, and 3D Printing can also help craft them. Companies like Sculpteo even offer 3D printed products that prevent electrostatic discharge or ESD.
This phenomenon occurs when surfaces come into contact and create static electricity. This reaction eventually causes ESD that damages components and ignites fires!
That’s when Sculpteo products come in handy. It helps in creating prototypes and facilitates research and development for other companies.
6. Education
Schools could provide enhanced learning opportunities with the help of 3D Printing. For example, let us say a science class teaches about how a car works.
Showing pictures of the components isn’t engaging, but bringing real examples to class isn’t viable. Instead, a teacher could just print a replica of each part.
The 3D-printed objects could move similarly to the real-life parts, so students could see up close how they move. What’s more, 3D Printing is an excellent tool for architecture students.
They could see how their designs look as physical structures instead of digital figures. They could look at structural issues or improvements not seen in 3D software models.
The production method could also foster creativity. High school students could use 3D Printing as an introduction to design courses to figure out if they want it as a career.
It’s also great for medical students because 3D Printing may reduce the need for studying genuine body parts. A class could simply print teeth or bones for study.
Different types of 3D printing methods

Photo Credit: 3dprintingindustry.com
We just looked at the wide range of applications for Printing 3D objects, but how does the process work? We need to elaborate on it to have a better understanding.
We will go through the nine 3D printing methods available right now. Look at the following list and read their descriptions:
- Fused deposition modeling
- Binder jetting
- Material jetting
- Selective deposition lamination
- Stereolithography
- Digital light processing
- Direct metal laser sintering
- Selective laser melting
- Electron beam melting
1. Fused deposition modeling
If you’re familiar with 3D Printing, you’ve probably seen it in an online video. Such clips often show a machine pouring thin strips of plastic into the shape of a 3D object.
The device starts from the bottom, applying more molten plastic and working its way up. This method is the gist of how fused deposition modeling works.
Watch this process in action, and you might notice that it has a few plastic supports sticking out. The machine adds these extra bits to keep flimsy parts in place.
Once it finishes a model, the user snips off the supports. You can compare this 3D-printed model to a plastic toy model kit. Each part is tiny, so a plastic frame secures each one.
You detach that frame first to assemble the pieces into a finished product. The same principles apply to FDM, also known as fused filament fabrication.
You could build separate components via 3D Printing, detach their supports, then construct them into a large or complex object.
Fused deposition modeling is one of the 3D printing methods accessible to regular folks. Unfortunately, it’s not great for creating objects with fine details. The plastic contracts as it cools, causing a detailed logo or a similar design to look misshapen in the final build.
Depending on your 3D model, you might have to add more plastic frames. As a result, you’ll have to cut or “weed” out more of them, so you waste more plastic.
2. Binder jetting
This 3D printing technique involves jet heads, a binding agent or binder, and sheets of powdered material. Here are the simplified steps of how binder jetting works:
- The printer starts with a platform with a thin layer of powder.
- Jet heads apply the binder to specific sections to create a layer.
- Then, a roller applies a new powder coat for the next layer.
- The 3D printer repeats steps one to three until it creates a new object.
The cool thing about this 3D printing method is that it can use food and ceramics as materials. That’s why some restaurants offer 3D-printed desserts like candies and chocolates.
You can also choose the colors by adding them to the binder. The downside is that it’s not as strong as the other additive manufacturing methods that melt the materials.
This 3D printing process requires additional post-processing methods, such as UV light treatment. Still, binder jetting might be enough if you just want to boost your cooking skills with 3D Printing.
3. Material jetting
This next additive manufacturing method emphasizes its “manufacturing” namesake. Material jetting lets you create 3D objects made with soft and hard plastics.
Such a feature is crucial if you want to create a prototype or test sample of your product. This 3D printing process is similar to binder jetting, except it can divide layers into different textures.
Let’s say you created a smartphone case. You could make the edges soft to grip them more securely. Material jetting lets you create such projects.
It could start by building the rigid body of that case. The process will cure that component with UV light, so the first layer hardens. Afterward, this 3D printing method will apply soft edges.
The major problem with this 3D printing process is that the parts tend to break easily. The entire product will quickly degrade over time. Still, this process is an excellent option if you need rapid prototyping.
4. Selective deposition lamination
This additive manufacturing process sets itself apart since it uses paper. Selective deposition lamination uses the one commonly used for regular printers. Here are the simplified steps of how it works:
- An SDL machine starts by adding a single sheet of paper to a platform.
- Then, it applies an adhesive to some regions of the sheet.
- The machine applies heat and pressure to the sheet.
- The SDL machine uses a tungsten carbide blade to cut the sheets one at a time.
- Some printer models apply color to each layer, so the final product has more details.
- Repeat steps one to four until the machine finishes the model.
Like other 3D printing techniques, SDL models have support structures made of paper. As a result, they are much more convenient to trim than plastic ones.
Selective deposition lamination has some flaws. First, it doesn’t allow for complex shapes. Second, the machines can only use a set number of sheets, limiting the size of 3D-printed models.
5. Stereolithography
Stereolithography is the most accurate 3D printing method right now. Read the following list to see how the process works:
- The user refills a stereolithography machine with liquid resin.
- Then, the device lowers a metal surface onto the resin tank.
- The upper platform slowly rises as a laser beneath the lower container fires at specific points of the liquid. This process allows the machine to create a 3D object layer by layer.
This 3D printing technique can produce the most complex objects while applying a superb surface finish. The problem is that the models can easily break.
That’s why the final model has so many plastic supports. Some need post-processing to harden the resin models and turn them into viable prototypes.
6. Digital light processing
This 3D printing style works like stereolithography, except it uses a more conventional light source like an arc lamp. The resin platform has minuscule reflective surfaces that adjust so that they can shape each layer.
Digital light processing is much faster since it requires a smaller amount of resin for each layer. Also, the use of fewer materials minimizes waste for this additive process.
Final products from DLP can be as detailed as the ones from stereolithography. However, they still have support structures and require post-processing.
7. Direct metal laser sintering
We have discussed how 3D Printing can create industrial tools. That’s because methods like direct metal laser sintering produce metal products. Here’s how it works:
- A roller spreads metal powder into a thin layer.
- The DMLS machine fires a laser beam to harden the layer at specific points.
- Afterward, the roller places a new coat on the metal powder bed.
- The machine repeats steps one to three until it creates a finished product.
The most significant advantage of this 3D printing method is that it does not attach support structures to the finished products. The excess powder holds each layer in place, so the final product stands independently.
The term “sintering” means applying enough heat to bond metals together. As a result, the finished products from DMLS need some time to cool.
Unlike stereolithography, this 3D printing process leaves a rough surface. Also known as selective laser sintering, it is a poor choice if you want detailed 3D models.
8. Selective laser melting
Selective laser melting 3D printing technique is similar to laser sintering. It fires a laser on a powder bed to create layers of metal products.
It uses much more energy since melting uses more heat than sintering. Yet, the final product is durable enough for aeronautics projects from NASA.
This 3D printing technique only works for steel, aluminum, cobalt, and titanium. Since it builds using layers from a powder bed, it can have varying temperatures.
As a result, the finished product may not become as sturdy as expected. Along with the high energy requirement, this is a costly 3D printing method.
9. Electron beam melting
This 3D printing method is similar to direct laser sintering and melting, except it uses an electron beam instead of a laser. Airborne particles could interfere with its rays, so EBM machines have a vacuum-sealed chamber.
The process can create highly dense medical-grade products such as implants. At the time of writing, EBM only sees wide use in the medical industry.
Still, the automobile and aerospace sectors are also checking how to use this type of 3D Printing. We may see this happen soon, considering how many methods we now have!
Benefits of using 3D printers
Photo Credit: newatlas.com
The great thing about this additive method is that it has become more accessible to the public. You can get your first 3D printer for as low as $200. Here are some reasons why it’s a good idea to purchase one:
- Printing 3D models can be fun! A printer could create nearly anything you can imagine.
- This process can also hone your creativity since you can create and improve designs whenever you want.
- You can create a model whenever you want. Depending on your skill, you could build architectural scale models.
- You determine how much material you will use for the project. As a result, 3D Printing is a cost-effective way to make arts and crafts while reducing waste.
- What’s more, you could create stuff out of metal and plastic. In other words, this product development process is highly versatile.
- 3D Printing at home lets you create prototypes quickly.
- Depending on your 3D printer, you could start projects anywhere. The portability makes it easier for you to use 3D Printing as a business opportunity.
Tips before buying a 3D printer
You will have to think of certain factors before purchasing your first 3D printer. Read the following list to learn more:
- You could buy a cheap machine for $200, but those have the most rudimentary features. Also, you will have to tweak a lot of stuff before it is ready for use.
- Make sure you will create a lot of projects with your device. If you just need one for a one-off model, it’s best not to purchase one.
- You need to have experience with computer-aided design or CAD software. This skill can be a steep learning curve for 3D Printing.
- 3D Printing requires a well-ventilated area to let the plastic odor out of your home. Otherwise, you might breathe in the particles from your printer, causing health issues.
- The device makes a lot of noise that could disturb other people in your home.
- Regular 3D printers are affordable because they leave the moving parts exposed.
- It is not easy to find repairers for your 3D printer. These devices could encounter issues within a few hours, so expect to fix things yourself.
- Most importantly, you will need enough creativity to make stuff from 3D Printing.
Read More: The Best Printers And PCs On Amazon
Can I start without a 3D printer?
It is still a good idea to learn 3D Printing since it will become more prevalent in the future. You could learn skills to find new passions or open job opportunities.
Fortunately, you will not have to buy a printer for it. You can find various companies such as Shapeways and You3Dit that can create 3D models for you.
Send your computer-aided design, and these businesses will give you a price quote. The required payment will also depend on your chosen powder particles or other materials.
Pay that amount, and they will deliver the finished product to your home after a few days. These companies use industrial-grade equipment, so you avoid trial and error.
As mentioned earlier, 3D Printing is more common nowadays. You might find nearby stores that offer this service. Some US postal offices like FedEx have 3D printers.
Heading to these locations could be another cost-effective way of 3D Printing. Aside from that, you might want to visit your local library. Believe it or not, some libraries have 3D printers.
They often let people use it for free. You will have to bring the materials yourself, though. Still, this method is a great way to learn 3D Printing.
Related Articles
Final thoughts
Nowadays, 3D Printing is changing how we manufacture things. It lets people create prototypes quickly to offer new and exciting products to customers.
It now has a wide range of applications, from aerospace to education. Products that took months to create can now complete within days, thanks to 3D Printing.
More importantly, you can learn this new manufacturing process yourself. You could go to stores that provide the feature, or you may buy a 3D printer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is 3D Printing, and how does the process work?
It creates products layer by layer with the help of plastic powders, metal particles, or liquid resin. Then, a 3D printer applies light layer by layer until it creates a finished model.
How much will it cost to 3D print?
You could start by purchasing a 3D printer worth $200. Alternatively, you can try local stores and libraries for more cost-effective methods.
What are the uses for 3D Printing?
A 3D printer can create medical devices such as hearing aids. It is also instrumental in making the design of production cycles of industrial manufacturing much faster.
What software do I need for 3D Printing?
You will need a 3D modeling program like AutoCAD to make your designs. After that, you must get slicing software like Cura Slicer or Simplify3D. Fortunately, you can download them all on the internet.
Where can I buy a 3D printer?
You could purchase your first 3D printer from brick-and-mortar printer stores. On the other hand, you can order one from various online stores such as Amazon.

